Earth
ID: 13946
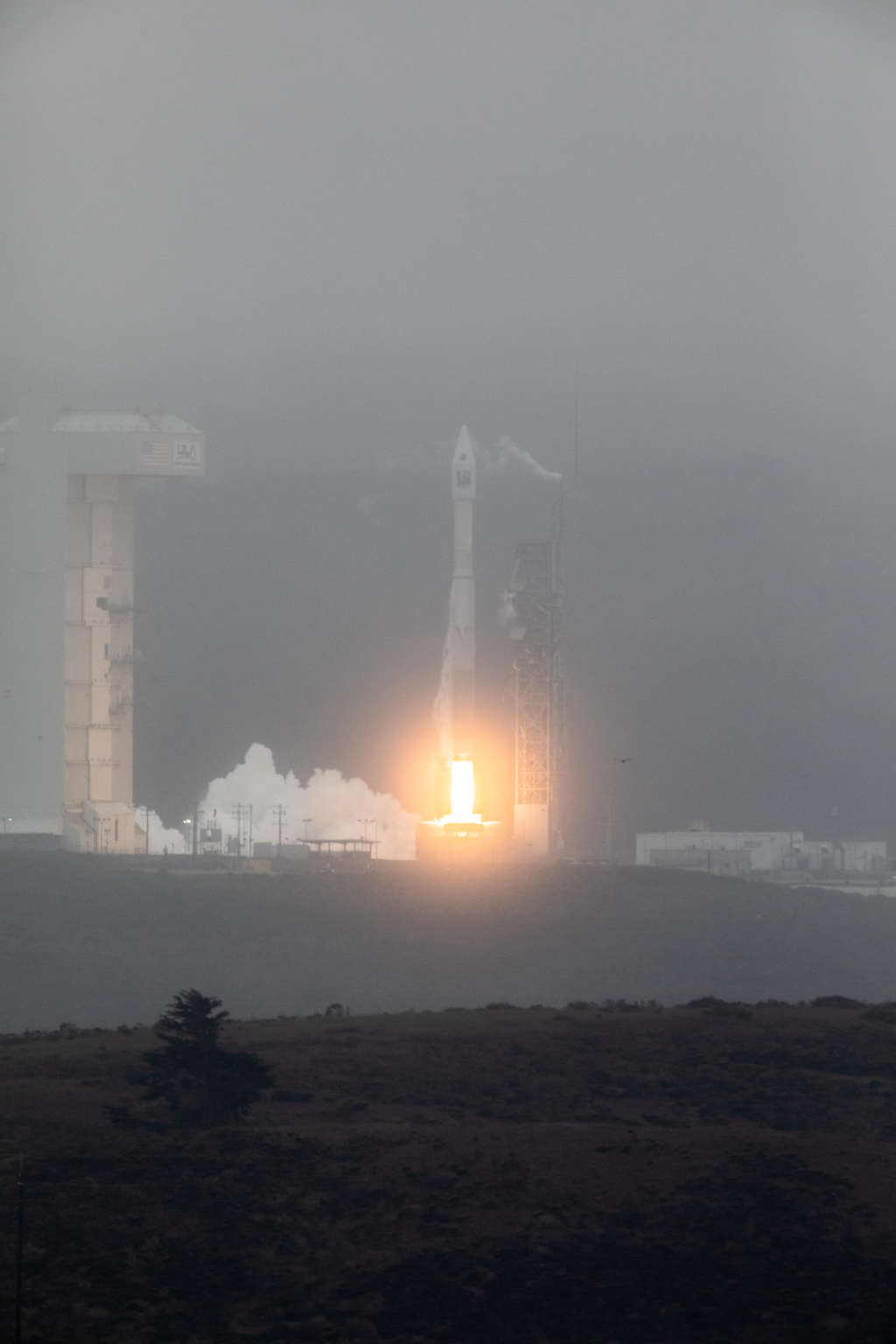
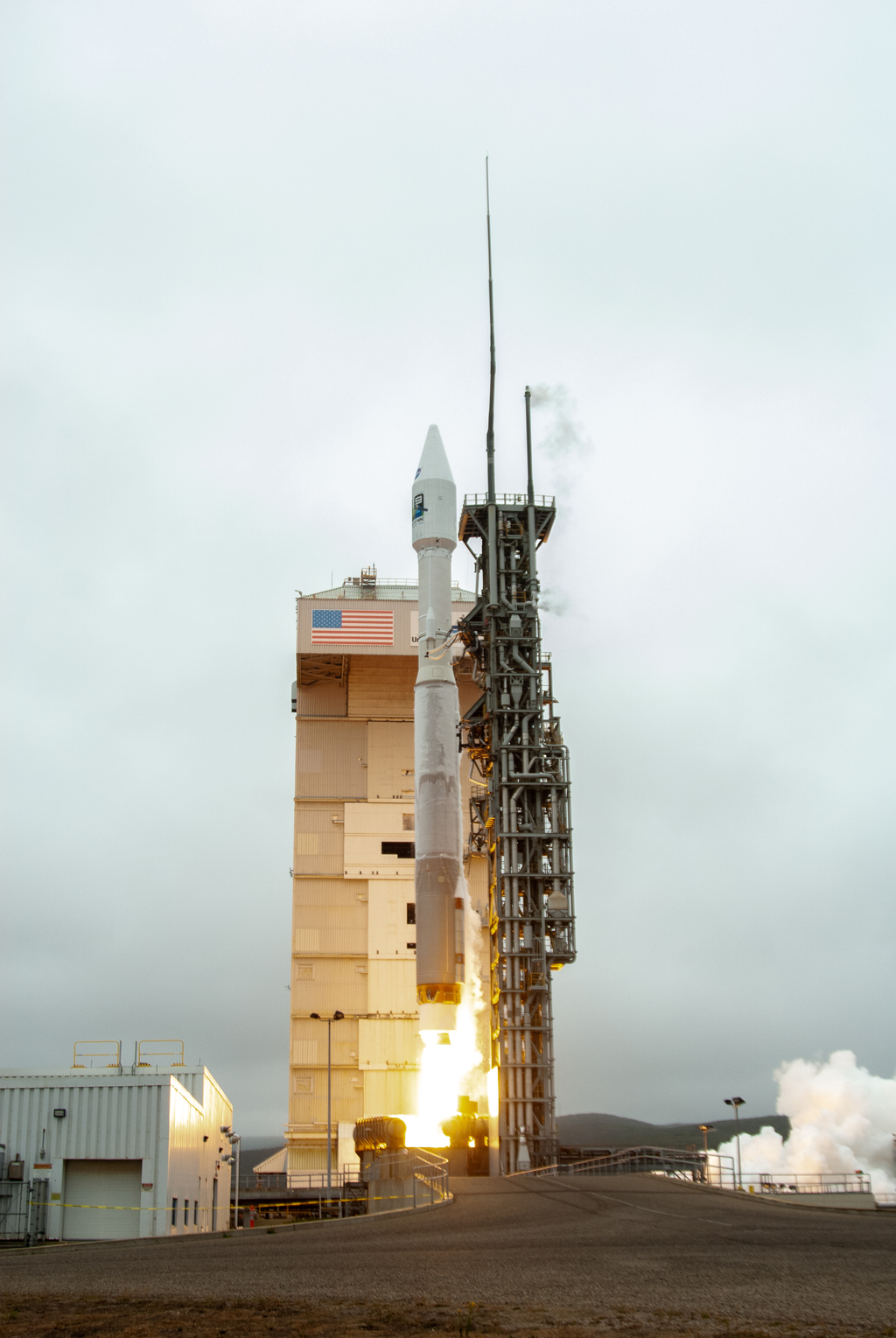
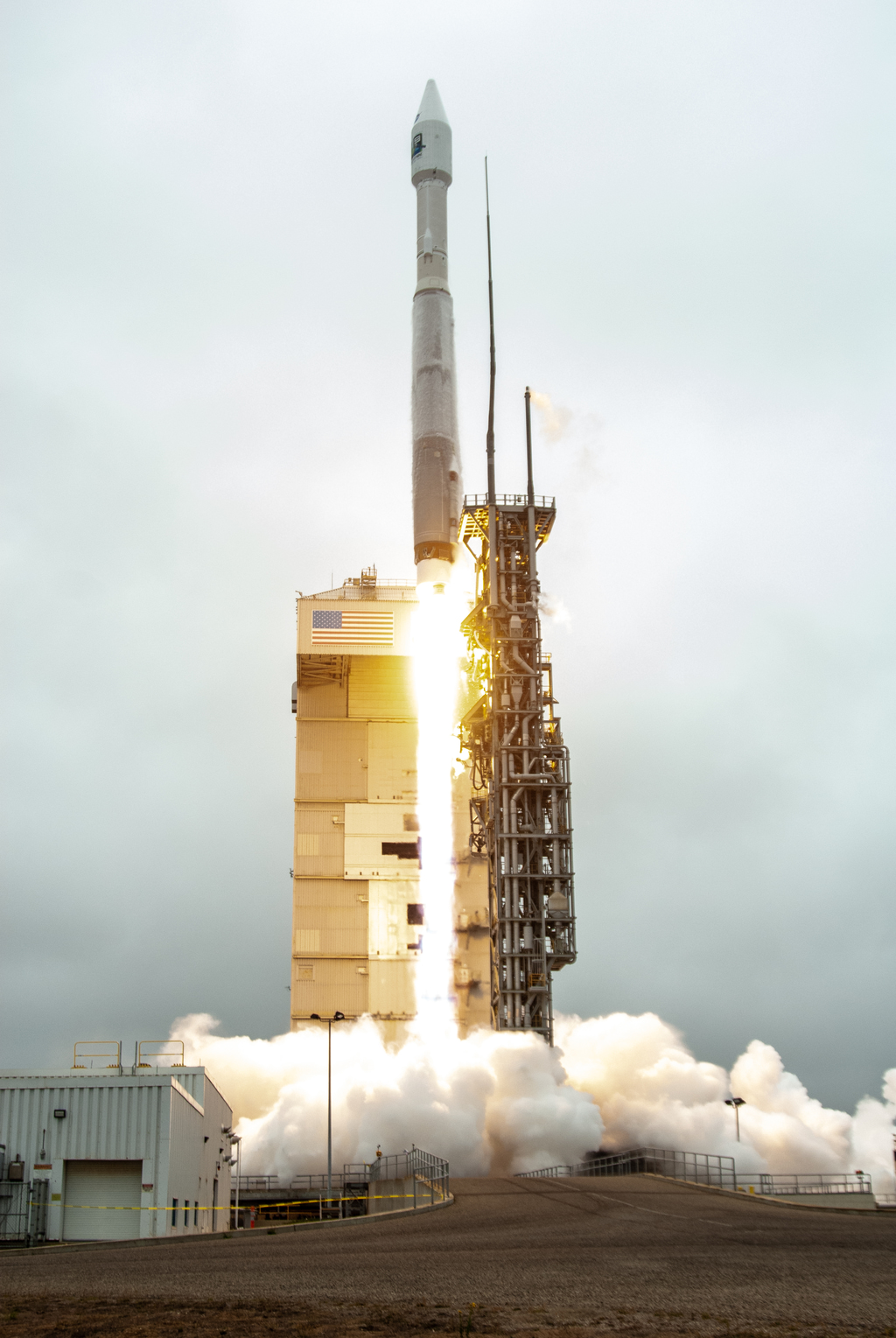
Landsat 9, a NASA satellite built to monitor the Earth’s land surface, successfully launched at 2:12 p.m. EDT Monday from Vandenberg Space Force Base in California.
A joint mission with the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS), Landsat 9 lifted off on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Vandenberg’s Space Launch Complex 3E. Norway’s Svalbard satellite-monitoring ground station acquired signals from the spacecraft about 83 minutes after launch. Landsat 9 is performing as expected as it travels to its final orbital altitude of 438 miles (705 kilometers).
Landsat 9 joins its sister satellite, Landsat 8, in orbit. Working in tandem, the two satellites will collect images spanning the entire planet every eight days.
The instruments aboard Landsat 9 – the Operational Land Imager 2 (OLI-2) and the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2 (TIRS-2) – measure 11 wavelengths of light reflected or radiated off Earth’s surface, in the visible spectrum as well as other wavelengths beyond what our eyes can detect. As the satellite orbits, these instruments will capture scenes across a swath of 115 miles (185 kilometers). Each pixel in these images represents an area about 98 feet (30 meters) across, about the size of a baseball infield. At that high a resolution, resource managers will be able to identify most crop fields in the United States.
The USGS Earth Resources Observation and Science (EROS) Center in Sioux Falls, South Dakota, processes and stores data from the instruments, continuously adding that information to the five decades of data from all of the Landsat satellites.
All Landsat images and the embedded data are free and publicly available, a policy that has resulted in more than 100 million downloads since its inception in 2008.
NASA manages the Landsat 9 mission. Teams from NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, also built and tested the TIRS-2 instrument. NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida managed the launch of the mission. EROS will operate the mission and manage the ground system, including maintaining the Landsat archive. Ball Aerospace in Boulder, Colorado, built and tested the OLI-2 instrument. United Launch Alliance is the rocket provider for Landsat 9’s launch. Northrop Grumman in Gilbert, Arizona, built the Landsat 9 spacecraft, integrated it with instruments, and tested it.
To learn more about Landsat 9, visit: https://www.nasa.gov/landsat9



Landsat 9 Launch Footage
A joint mission with the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS), Landsat 9 lifted off on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Vandenberg’s Space Launch Complex 3E. Norway’s Svalbard satellite-monitoring ground station acquired signals from the spacecraft about 83 minutes after launch. Landsat 9 is performing as expected as it travels to its final orbital altitude of 438 miles (705 kilometers).
Landsat 9 joins its sister satellite, Landsat 8, in orbit. Working in tandem, the two satellites will collect images spanning the entire planet every eight days.
The instruments aboard Landsat 9 – the Operational Land Imager 2 (OLI-2) and the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2 (TIRS-2) – measure 11 wavelengths of light reflected or radiated off Earth’s surface, in the visible spectrum as well as other wavelengths beyond what our eyes can detect. As the satellite orbits, these instruments will capture scenes across a swath of 115 miles (185 kilometers). Each pixel in these images represents an area about 98 feet (30 meters) across, about the size of a baseball infield. At that high a resolution, resource managers will be able to identify most crop fields in the United States.
The USGS Earth Resources Observation and Science (EROS) Center in Sioux Falls, South Dakota, processes and stores data from the instruments, continuously adding that information to the five decades of data from all of the Landsat satellites.
All Landsat images and the embedded data are free and publicly available, a policy that has resulted in more than 100 million downloads since its inception in 2008.
NASA manages the Landsat 9 mission. Teams from NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, also built and tested the TIRS-2 instrument. NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida managed the launch of the mission. EROS will operate the mission and manage the ground system, including maintaining the Landsat archive. Ball Aerospace in Boulder, Colorado, built and tested the OLI-2 instrument. United Launch Alliance is the rocket provider for Landsat 9’s launch. Northrop Grumman in Gilbert, Arizona, built the Landsat 9 spacecraft, integrated it with instruments, and tested it.
To learn more about Landsat 9, visit: https://www.nasa.gov/landsat9



Related
For More Information
Credits
Matthew Radcliff (KBRwyle): Lead Producer
Aaron E. Lepsch (ADNET Systems, Inc.): Technical Support
Jeffrey Masek (NASA/GSFC): Scientist
Del Jenstrom (NASA/GSFC): Project Manager
Aaron E. Lepsch (ADNET Systems, Inc.): Technical Support
Jeffrey Masek (NASA/GSFC): Scientist
Del Jenstrom (NASA/GSFC): Project Manager
Please give credit for this item to:
NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center
NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center
Short URL to share this page:
https://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/13946
Missions:
Landsat
Landsat 9
This item is part of this series:
Landsat
Keywords:
SVS >> HDTV
DLESE >> Human geography
SVS >> Landsat
DLESE >> Physical geography
GCMD >> Earth Science >> Land Surface
GCMD >> Earth Science >> Human Dimensions >> Land Use/Land Cover
GCMD >> Earth Science >> Land Surface >> Land Use/Land Cover
GCMD >> Earth Science >> Land Surface >> Land Use/Land Cover >> Land Use Classes
GCMD >> Earth Science >> Land Surface >> Landscape >> Landscape Pattern
SVS >> Launch
NASA Science >> Earth
SVS >> Vandenberg Air Force Base
GCMD keywords can be found on the Internet with the following citation: Olsen, L.M., G. Major, K. Shein, J. Scialdone, S. Ritz, T. Stevens, M. Morahan, A. Aleman, R. Vogel, S. Leicester, H. Weir, M. Meaux, S. Grebas, C.Solomon, M. Holland, T. Northcutt, R. A. Restrepo, R. Bilodeau, 2013. NASA/Global Change Master Directory (GCMD) Earth Science Keywords. Version 8.0.0.0.0
https://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/13946
Missions:
Landsat
Landsat 9
This item is part of this series:
Landsat
Keywords:
SVS >> HDTV
DLESE >> Human geography
SVS >> Landsat
DLESE >> Physical geography
GCMD >> Earth Science >> Land Surface
GCMD >> Earth Science >> Human Dimensions >> Land Use/Land Cover
GCMD >> Earth Science >> Land Surface >> Land Use/Land Cover
GCMD >> Earth Science >> Land Surface >> Land Use/Land Cover >> Land Use Classes
GCMD >> Earth Science >> Land Surface >> Landscape >> Landscape Pattern
SVS >> Launch
NASA Science >> Earth
SVS >> Vandenberg Air Force Base
GCMD keywords can be found on the Internet with the following citation: Olsen, L.M., G. Major, K. Shein, J. Scialdone, S. Ritz, T. Stevens, M. Morahan, A. Aleman, R. Vogel, S. Leicester, H. Weir, M. Meaux, S. Grebas, C.Solomon, M. Holland, T. Northcutt, R. A. Restrepo, R. Bilodeau, 2013. NASA/Global Change Master Directory (GCMD) Earth Science Keywords. Version 8.0.0.0.0