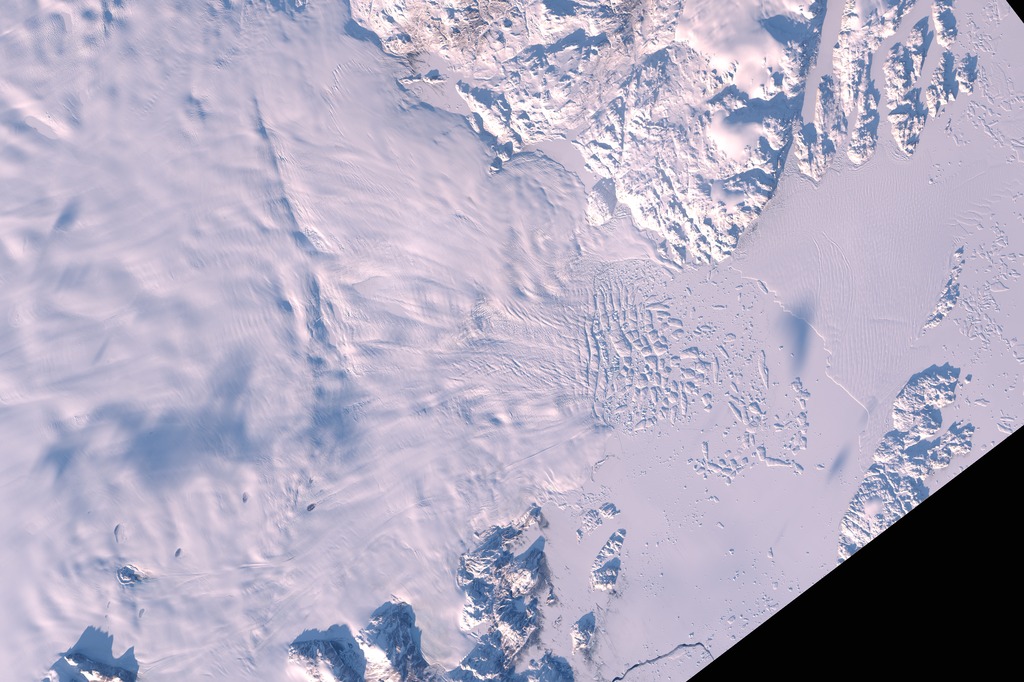
Changes in Zachariae Isstrom Glacier
There is a newer version of this story located here: https://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/31207
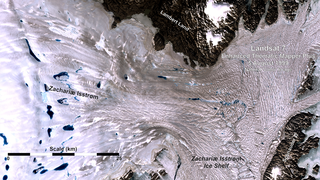
published November 2015 in Science found that Zachariæ Isstrøm broke loose from a stable position in 2012 and entered a phase of accelerated retreat.
The consequences will be felt for decades to come. The reason? Zachariæ Isstrøm is big. It drains ice from a 91,780 square kilometer (35,440 square mile) area of northeast Greenland. That’s about 5 percent of the Greenland Ice Sheet. The glacier holds enough water to raise global sea level by more than 46 centimeters (18 inches) if it were to melt completely. It is already shedding billions of tons of ice into the far North Atlantic each year.
“North Greenland glaciers are changing rapidly,” said lead author Jeremie Mouginot of the University of California, Irvine (UCI). “The shape and dynamics of Zachariæ Isstrøm have changed dramatically over the last few years. The glacier is now breaking up and calving high volumes of icebergs into the ocean, which will result in rising sea levels for decades to come.”
As of 2015, the glacier is losing 5 billion tons of ice every year. The time-lapse animation above shows the glacier’s retreat during the 2015 melt season. The animation is composed of 26 natural-color images acquired by Landsat 8 from May 19 through October 1, 2015.
To better understand the changes taking place at Zachariæ Isstrøm, Mouginot and his colleagues from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL), and the University of Kansas compiled an array of airborne and satellite data. The scientists determined that the bottom of Zachariæ Isstrøm is being rapidly eroded at the coast by warmer ocean water that mixes with growing amounts of meltwater from the ice sheet.
“Zachariæ Isstrøm is being hit from above and below,” said the study’s co-author Eric Rignot, who has a joint appointment at UCI and JPL. “The top of the glacier is melting away as a result of decades of steadily increasing air temperatures, while its underside is compromised by currents carrying warmer ocean water, and the glacier is now breaking away into bits and pieces and retreating into deeper ground.”
For more about this research, read JPL’s full feature story.
Newer Version
Credits
Jesse Allen (SSAI): Lead Visualizer
Kathryn Hansen (SSAI): Writer
Alan Buis (NASA/JPL CalTech): Writer
Brian Bell (UCI): Writer
NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center
https://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/30750
Missions:
Landsat
LDCM: Landsat Data Continuity Mission
This item is part of this series:
Landsat
Keywords:
SVS >> HDTV
SVS >> Landsat
GCMD >> Earth Science >> Cryosphere >> Glaciers/Ice Sheets
GCMD >> Earth Science >> Cryosphere >> Glaciers/Ice Sheets >> Glacier Motion/Ice Sheet Motion
GCMD >> Earth Science >> Cryosphere >> Glaciers/Ice Sheets >> Glaciers
GCMD >> Location >> Greenland
SVS >> Hyperwall
SVS >> Glaciers
NASA Science >> Earth
GCMD keywords can be found on the Internet with the following citation: Olsen, L.M., G. Major, K. Shein, J. Scialdone, S. Ritz, T. Stevens, M. Morahan, A. Aleman, R. Vogel, S. Leicester, H. Weir, M. Meaux, S. Grebas, C.Solomon, M. Holland, T. Northcutt, R. A. Restrepo, R. Bilodeau, 2013. NASA/Global Change Master Directory (GCMD) Earth Science Keywords. Version 8.0.0.0.0