Planets and Moons
ID: 20384
On Enceladus under a crust of ice lies a global ocean of salty water. Jets, supplied by that ocean, gush from the surface of the moon and feed into the entire system of Saturn.
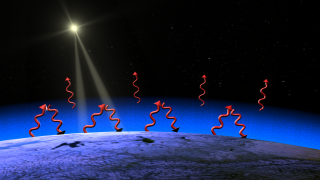
NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope first look at this ocean world is revealing that a plume spouts water out more than 20 times the size of the moon itself. Enceladus, together with its sub-surface ocean, is one of the most exciting scientific targets in our solar system in the search for life beyond Earth.
Sandwiched between the moon’s icy outer crust and its rocky core is a global reservoir of salty water. Geyser-like volcanos spew jets of ice particles, water vapor, and organic chemicals out of crevices in the moon’s surface informally called ‘tiger stripes.’
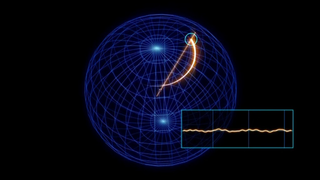
In this video, we show a possible scenario of how water could be being sourced from hydrothermal vents in the sub-surface ocean to generate the observed plumes.
Enceladus
NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope first look at this ocean world is revealing that a plume spouts water out more than 20 times the size of the moon itself. Enceladus, together with its sub-surface ocean, is one of the most exciting scientific targets in our solar system in the search for life beyond Earth.
Sandwiched between the moon’s icy outer crust and its rocky core is a global reservoir of salty water. Geyser-like volcanos spew jets of ice particles, water vapor, and organic chemicals out of crevices in the moon’s surface informally called ‘tiger stripes.’
In this video, we show a possible scenario of how water could be being sourced from hydrothermal vents in the sub-surface ocean to generate the observed plumes.
Animation Credits
Jenny McElligott (Advocates in Manpower Management, Inc.): Lead Animator
Aaron E. Lepsch (ADNET Systems, Inc.): Technical Support
Geronimo Villanueva (Catholic University of America): Lead Scientist
Michael Lentz (KBR Wyle Services, LLC): Lead Art Director
Walt Feimer (KBR Wyle Services, LLC): Lead Project Manager
Aaron E. Lepsch (ADNET Systems, Inc.): Technical Support
Geronimo Villanueva (Catholic University of America): Lead Scientist
Michael Lentz (KBR Wyle Services, LLC): Lead Art Director
Walt Feimer (KBR Wyle Services, LLC): Lead Project Manager
Please give credit for this item to:
NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center Conceptual Image Lab
NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center Conceptual Image Lab
Short URL to share this page:
https://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/20384
Keywords:
SVS >> James Webb Space Telescope
NASA Science >> Planets and Moons
SVS >> Saturn
SVS >> Enceladus
https://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/20384
Keywords:
SVS >> James Webb Space Telescope
NASA Science >> Planets and Moons
SVS >> Saturn
SVS >> Enceladus