Sun
ID: 13714
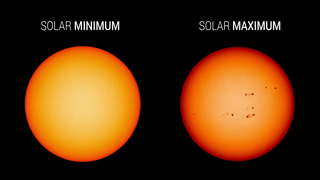
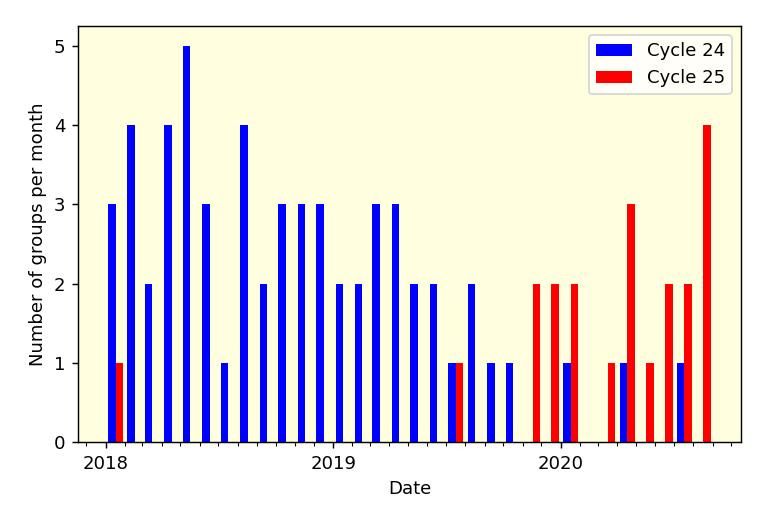
Solar Cycle 25 has begun. The Solar Cycle 25 Prediction Panel announced solar minimum occurred in December 2019, marking the transition into a new solar cycle. In a press event, experts from the panel, NASA, and NOAA discussed the analysis and Solar Cycle 25 prediction, and how the rise to the next solar maximum and subsequent upswing in space weather will impact our lives and technology on Earth.
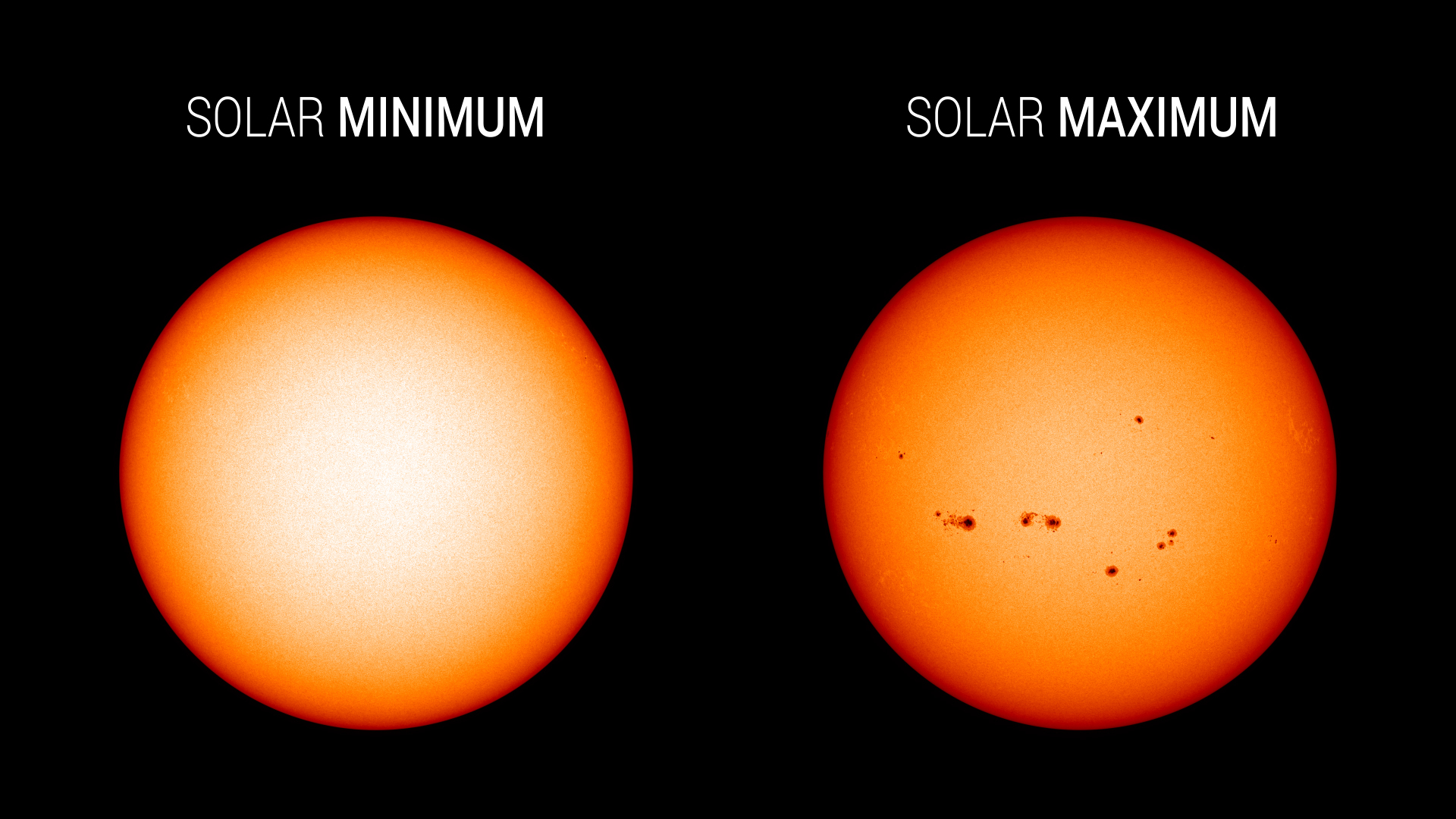
A new solar cycle comes roughly every 11 years. Over the course of each cycle, the star transitions from relatively calm to active and stormy, and then quiet again; at its peak, the Sun’s magnetic poles flip. Now that the star has passed solar minimum, scientists expect the Sun will grow increasingly active in the months and years to come.
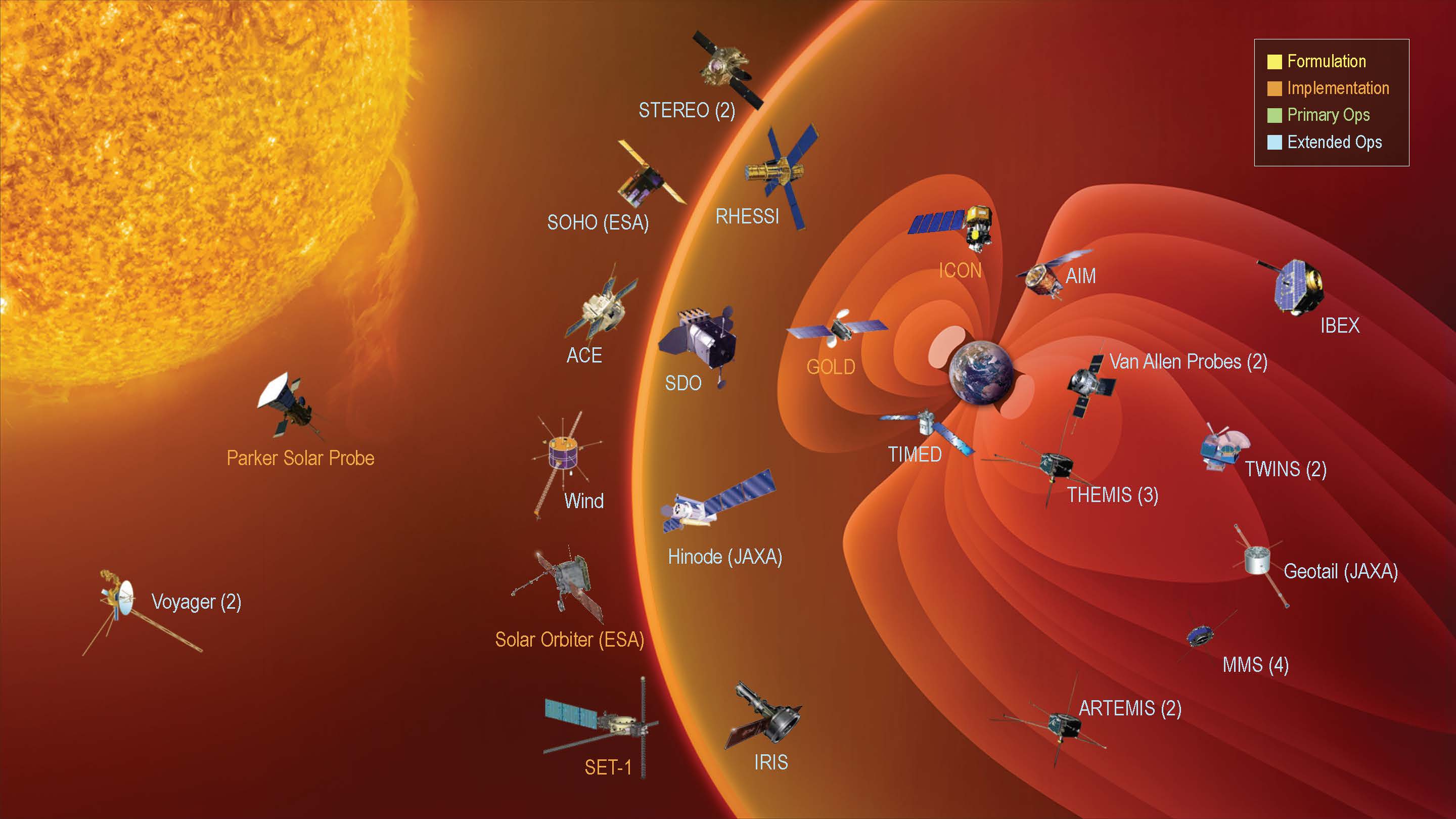
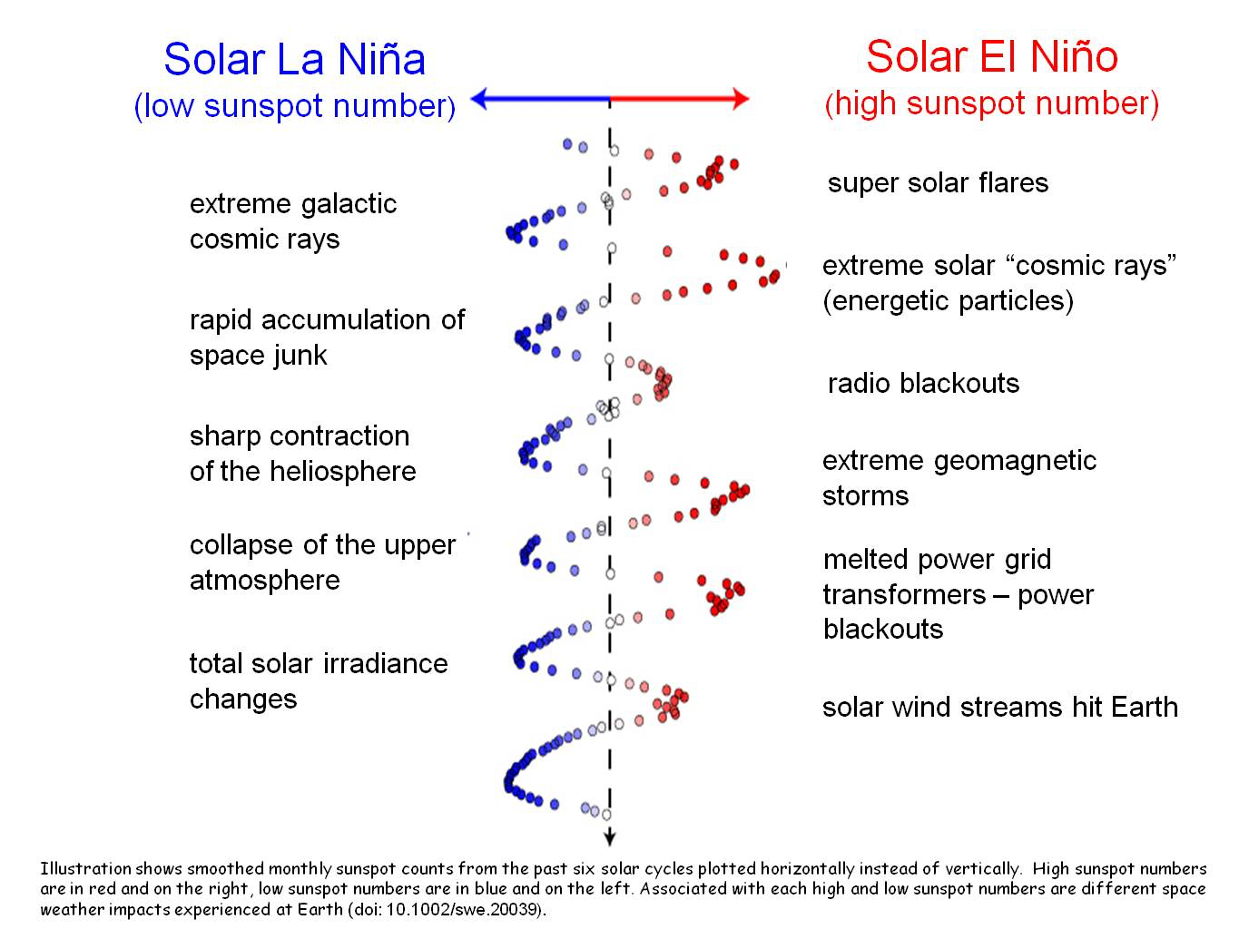
Understanding the Sun’s behavior is an important part of life in our solar system. The Sun’s outbursts—including eruptions known as solar flares and coronal mass ejections—can disturb the satellites and communications signals traveling around Earth, or one day, Artemis astronauts exploring distant worlds. Scientists study the solar cycle so we can better predict solar activity.
Click here for the NOAA press kit.
Listen to the media telecon.
Participants:
• Lisa Upton, Co-chair, Solar Cycle 25 Prediction Panel; Solar Physicist, Space Systems Research Corporation
• Doug Biesecker, Solar Physicist, NOAA’s Space Weather Prediction Center; Co-chair, Solar Cycle 25 Prediction Panel
• Elsayed Talaat, Director, Office of Projects, Planning and Analysis; NOAA’s Satellite and Information Service
• Lika Guhathakurta, Heliophysicist, Heliophysics Division, NASA Headquarters
• Jake Bleacher, Chief Exploration Scientist, NASA Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate




Solar Cycle 25 Is Here. NASA, NOAA Scientists Explain What This Means
A new solar cycle comes roughly every 11 years. Over the course of each cycle, the star transitions from relatively calm to active and stormy, and then quiet again; at its peak, the Sun’s magnetic poles flip. Now that the star has passed solar minimum, scientists expect the Sun will grow increasingly active in the months and years to come.
Understanding the Sun’s behavior is an important part of life in our solar system. The Sun’s outbursts—including eruptions known as solar flares and coronal mass ejections—can disturb the satellites and communications signals traveling around Earth, or one day, Artemis astronauts exploring distant worlds. Scientists study the solar cycle so we can better predict solar activity.
Click here for the NOAA press kit.
Listen to the media telecon.
Participants:
• Lisa Upton, Co-chair, Solar Cycle 25 Prediction Panel; Solar Physicist, Space Systems Research Corporation
• Doug Biesecker, Solar Physicist, NOAA’s Space Weather Prediction Center; Co-chair, Solar Cycle 25 Prediction Panel
• Elsayed Talaat, Director, Office of Projects, Planning and Analysis; NOAA’s Satellite and Information Service
• Lika Guhathakurta, Heliophysicist, Heliophysics Division, NASA Headquarters
• Jake Bleacher, Chief Exploration Scientist, NASA Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate








Used Elsewhere In
Related
For More Information
Credits
Producers:
Joy Ng (USRA)
Kathalina Tran (SGT)
Karen Fox (ADNET Systems, Inc.)
Technical Support:
Aaron E. Lepsch (ADNET Systems, Inc.)
Joy Ng (USRA)
Kathalina Tran (SGT)
Karen Fox (ADNET Systems, Inc.)
Technical Support:
Aaron E. Lepsch (ADNET Systems, Inc.)
Please give credit for this item to:
NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center
NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center
Short URL to share this page:
https://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/13714
Mission:
Artemis Program (Human Spaceflight — Moon to Mars)
Keywords:
SVS >> HDTV
SVS >> Solar Cycle
SVS >> Solar Wind
SVS >> Space Weather
SVS >> SDO
SVS >> Solar Dynamics Observatory
SVS >> Heliophysics
SVS >> GEOS
SVS >> Sunspot Cycle
SVS >> Corona
NASA Science >> Sun
SVS >> Solar Cycle 25
SVS >> Sunspot Number
SVS >> Solar Minimum
SVS >> Solar Maximum
SVS >> SWPC
SVS >> Gateway
https://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/13714
Mission:
Artemis Program (Human Spaceflight — Moon to Mars)
Keywords:
SVS >> HDTV
SVS >> Solar Cycle
SVS >> Solar Wind
SVS >> Space Weather
SVS >> SDO
SVS >> Solar Dynamics Observatory
SVS >> Heliophysics
SVS >> GEOS
SVS >> Sunspot Cycle
SVS >> Corona
NASA Science >> Sun
SVS >> Solar Cycle 25
SVS >> Sunspot Number
SVS >> Solar Minimum
SVS >> Solar Maximum
SVS >> SWPC
SVS >> Gateway