Sun
Planets and Moons
ID: 12557

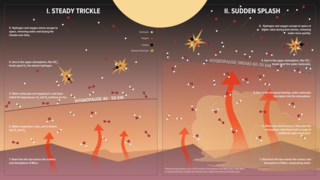
Solar wind and radiation are responsible for stripping the Martian atmosphere, according to results from NASA's MAVEN mission. By measuring light and heavy isotopes of argon in the Martian atmosphere, scientists have determined that the majority of the planet's air and water were removed to space by sputtering. In this process, ions from the Mars atmosphere get picked up by the solar wind and slammed into other atoms at the top of the atmosphere, knocking them into space.
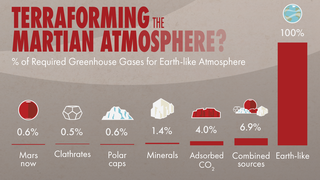
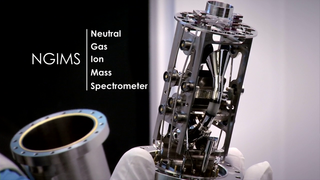
Scientists used measurements of light and heavy argon from MAVEN and NASA's Curiosity rover to determine that sputtering has removed 65% of Mars' argon to space, along with the majority of other gases like carbon dioxide. Over billions of years, this transformed Mars from a hospitable environment into the cold, dry planet that we see today.
Learn more about the MAVEN argon loss finding.
MAVEN Reveals Mars Argon Loss to Space

Scientists used measurements of light and heavy argon from MAVEN and NASA's Curiosity rover to determine that sputtering has removed 65% of Mars' argon to space, along with the majority of other gases like carbon dioxide. Over billions of years, this transformed Mars from a hospitable environment into the cold, dry planet that we see today.
Learn more about the MAVEN argon loss finding.
Related
For More Information
Related Documentation
Credits
Bruce Jakosky (LASP): Scientist
Lisa Poje (USRA): Lead Animator
Dan Gallagher (USRA): Producer
William Steigerwald (NASA/GSFC): Science Writer
Walt Feimer (KBR Wyle Services, LLC): Animator
Michael Lentz (USRA): Animator
Chris Smith (SLAC): Animator
Matthew R. Radcliff (USRA): Support
Aaron E. Lepsch (ADNET Systems, Inc.): Technical Support
Lisa Poje (USRA): Lead Animator
Dan Gallagher (USRA): Producer
William Steigerwald (NASA/GSFC): Science Writer
Walt Feimer (KBR Wyle Services, LLC): Animator
Michael Lentz (USRA): Animator
Chris Smith (SLAC): Animator
Matthew R. Radcliff (USRA): Support
Aaron E. Lepsch (ADNET Systems, Inc.): Technical Support
Please give credit for this item to:
NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center
NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center
Short URL to share this page:
https://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/12557
Mission:
MAVEN: Mars Atmosphere and Volatile EvolutioN
Keywords:
SVS >> Climate
SVS >> HDTV
SVS >> Mars
SVS >> Hyperwall
SVS >> Planets
SVS >> Climate Change
SVS >> MAVEN
SVS >> Planetary Science
SVS >> Solar System >> Planets >> Mars >> Atmosphere
NASA Science >> Sun
NASA Science >> Planets and Moons
SVS >> Sputtering
SVS >> Argon
SVS >> Isotope
https://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/12557
Mission:
MAVEN: Mars Atmosphere and Volatile EvolutioN
Keywords:
SVS >> Climate
SVS >> HDTV
SVS >> Mars
SVS >> Hyperwall
SVS >> Planets
SVS >> Climate Change
SVS >> MAVEN
SVS >> Planetary Science
SVS >> Solar System >> Planets >> Mars >> Atmosphere
NASA Science >> Sun
NASA Science >> Planets and Moons
SVS >> Sputtering
SVS >> Argon
SVS >> Isotope