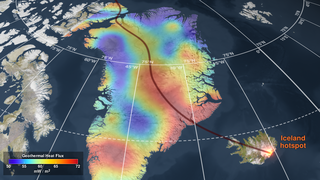
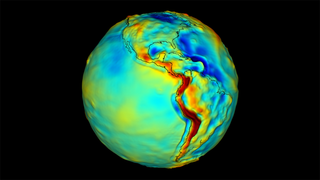
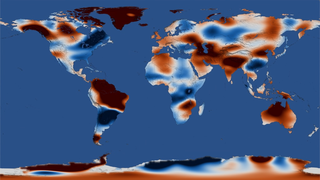
Universe
ID: 11545
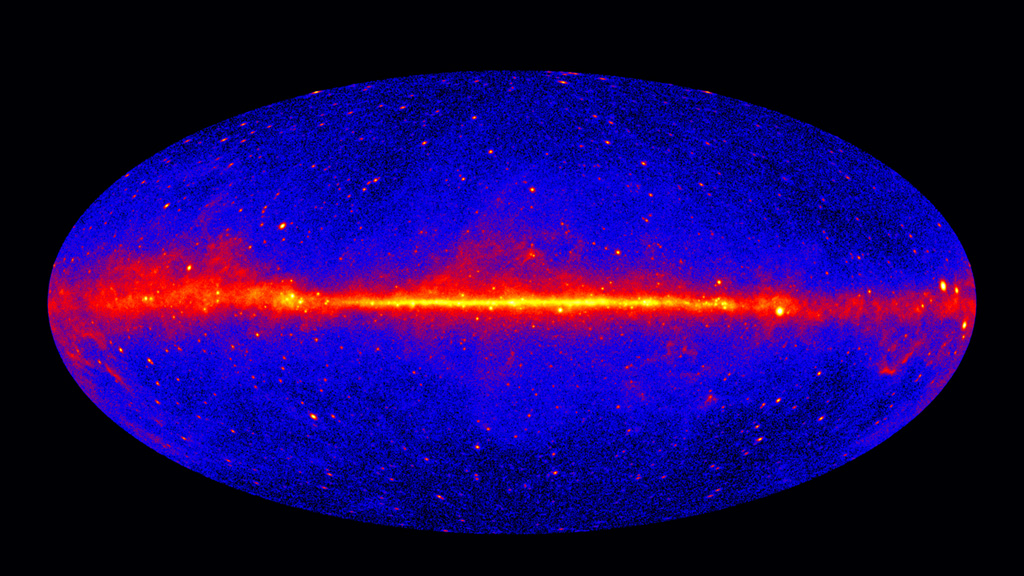
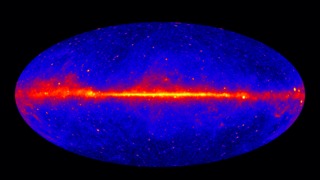
Gamma rays are the most powerful form of light in the universe. In the darkness of space, these luminous rays, which are invisible to humans but detectable by spacecraft, act as celestial beacons that alert us to some of the most extreme events and objects in the cosmos. For instance, when dying stars explode as supernovae, they emit gamma rays; so do particles being sucked into supermassive black holes; as do pulsars, the rapidly rotating stars that are as massive as our sun but only about the size of Manhattan. Since 2008, NASA’s Fermi spacecraft has observed gamma rays in the Milky Way and beyond. Plotted on a map, the locations of different sources appear as bright spots in the night sky. Watch the video to see how the spacecraft detects gamma rays.
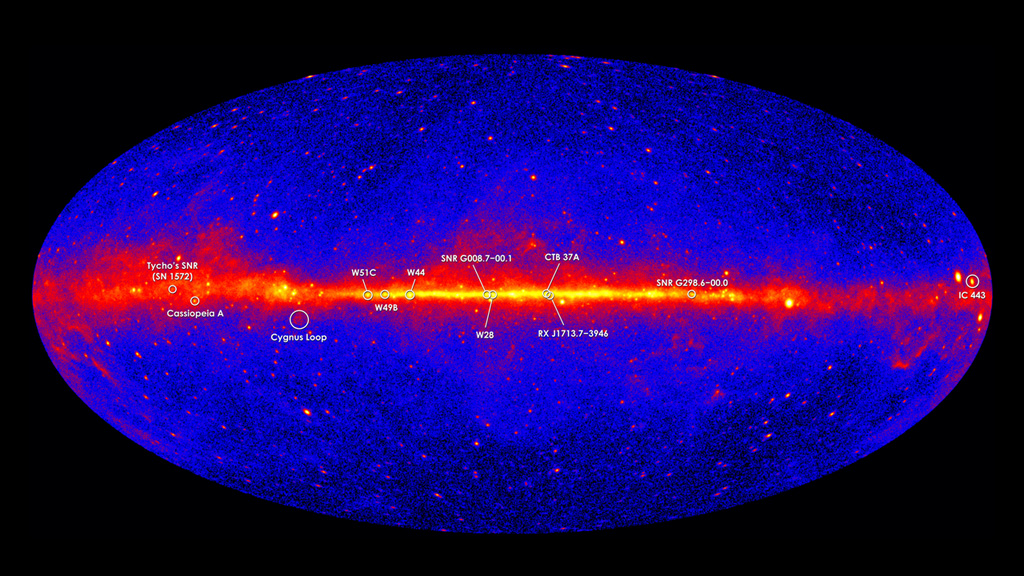
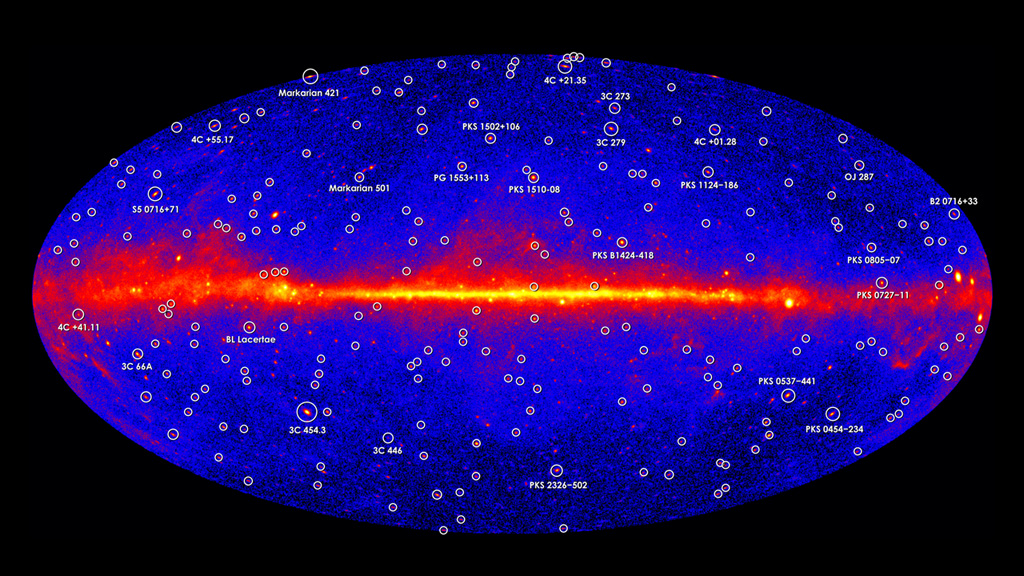
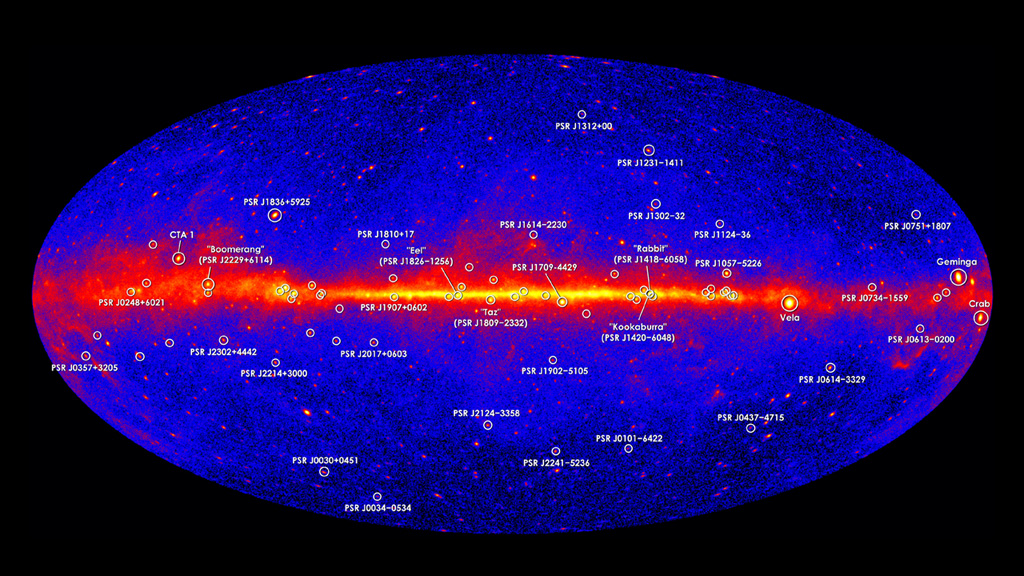

The Gamma-ray Sky





Related Stories
Story Credits
Visualizer/Animator:
Francis Reddy (University of Maryland College Park)
Producer:
Scott Wiessinger (USRA)
Lead Writer:
Matt Davenport (USRA)
Writer:
Francis Reddy (University of Maryland College Park)
Francis Reddy (University of Maryland College Park)
Producer:
Scott Wiessinger (USRA)
Lead Writer:
Matt Davenport (USRA)
Writer:
Francis Reddy (University of Maryland College Park)
Please give credit for this item to:
NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center
Images courtesy of NASA/DOE/Fermi LAT Collaboration
NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center
Images courtesy of NASA/DOE/Fermi LAT Collaboration
Short URL to share this page:
https://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/11545
Keywords:
SVS >> App
NASA Science >> Universe
https://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/11545
Keywords:
SVS >> App
NASA Science >> Universe