Methane plumes detected by EMIT Space Mission
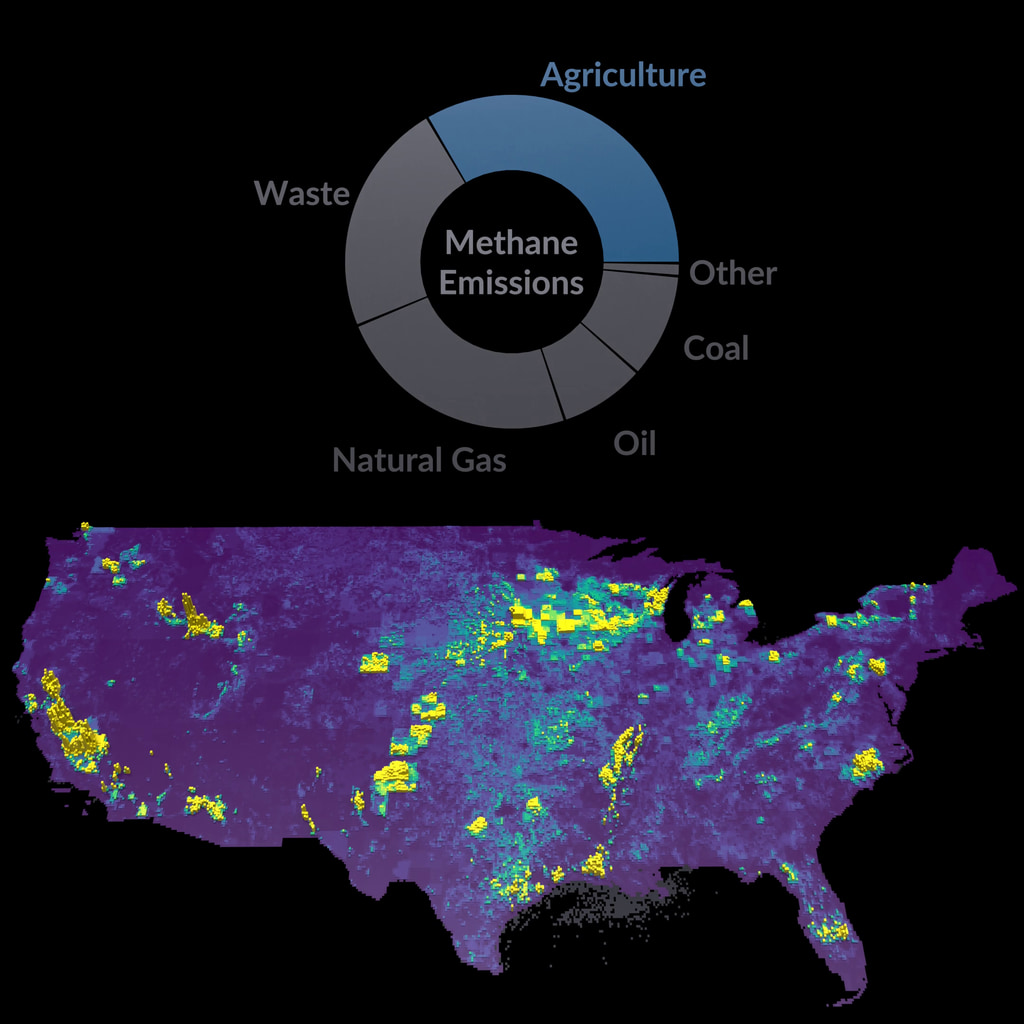
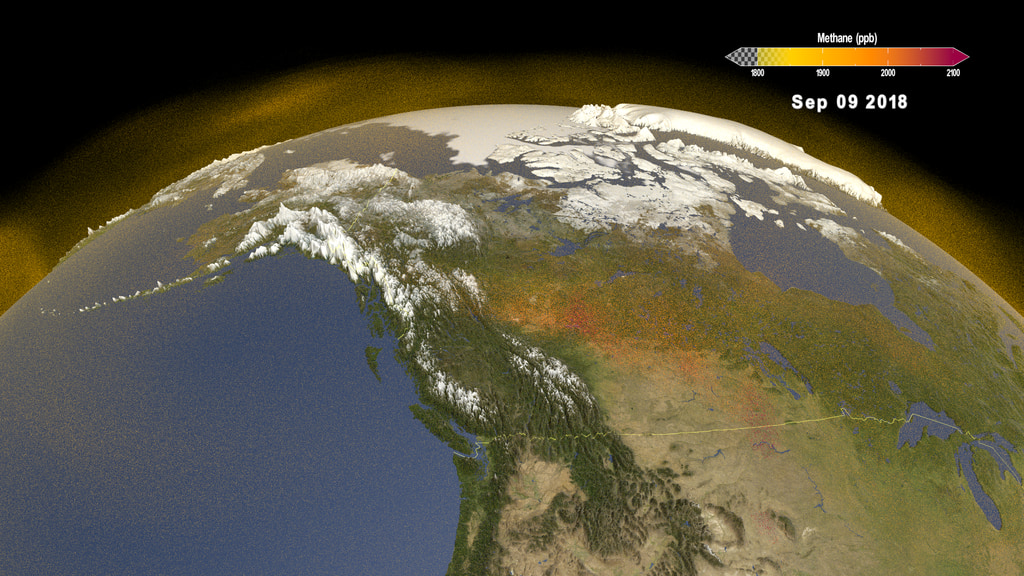
The Earth Surface Mineral Dust Source Investigation (EMIT) mission uses an imaging spectrometer to detect the unique pattern of reflected and absorbed light – called a spectral fingerprint – from various materials on Earth's surface and in its atmosphere. Perched on the International Space Station, EMIT was originally intended to map the prevalence of minerals in Earth's arid regions, such as the deserts of Africa and Australia. Scientists verified that EMIT could also detect the spectral fingerprints of methane and carbon dioxide which enables mapping of emissions from the energy, waste, and agriculture sectors.

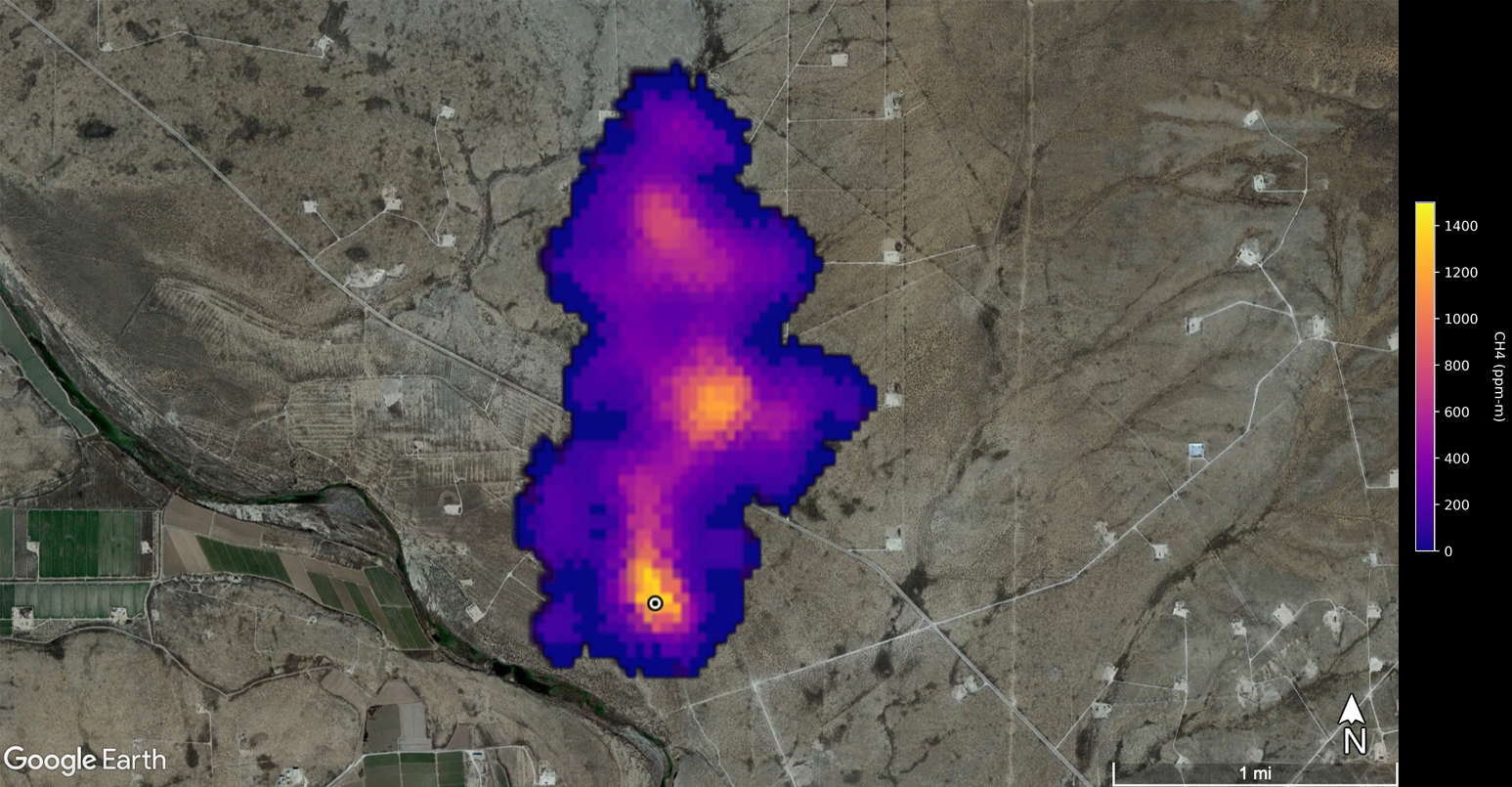
A region of enhanced methane is visible near Modesto, California.
This version of the data visualization includes location label.

A region of enhanced methane is visible near Modesto, California.

Two methane plumes were observed near Evanston, Wyoming.
This version of the data visualization includes location label.

Two methane plumes were observed near Evanston, Wyoming.

A plume of methane is detected near Rock Creek, Alabama.
This version of the data visualization includes location label.

A plume of methane is detected near Rock Creek, Alabama.
Data visualization showcasing methane plumes detected near Amman, Jordan during the period 10 August 2022-16 October 2023.
This version of the data visualization includes location label.
Data visualization showcasing methane plumes detected near Amman, Jordan during the period 10 August 2022-16 October 2023.
For More Information
Credits
Please give credit for this item to:
NASA's Scientific Visualization Studio
Visualizers
- Zoey N. Armstrong (Navteca, LLC.)
- Helen-Nicole Kostis (USRA)
Research technologist
- Andrew Thorpe (NASA/JPL, California Institute of Technology)
Technical support
- Laurence Schuler (ADNET Systems, Inc.)
- Ian Jones (ADNET Systems, Inc.)
Release date
This page was originally published on Tuesday, May 21, 2024.
This page was last updated on Monday, May 20, 2024 at 2:59 PM EDT.
Datasets used in this visualization
VISIONS: The EMIT Open Data Portal [International Space Station (ISS): Earth Surface Mineral Dust Source Investigation (EMIT)]
ID: 1210The Earth Surface Mineral Dust Source Investigation (EMIT) instrument measures surface mineralogy, targeting the Earth’s arid dust source regions. EMIT is installed on the International Space Station (ISS) and uses imaging spectroscopy to take measurements of the sunlit regions of interest between 52° N latitude and 52° S latitude.
Credit: Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology
This dataset can be found at: https://earth.jpl.nasa.gov/emit/data/data-portal/Greenhouse-Gases/
See all pages that use this dataset
Note: While we identify the data sets used in these visualizations, we do not store any further details, nor the data sets themselves on our site.