A newer version of this visualization is available.
The 2013 Earth-Orbiting Heliophysics Fleet
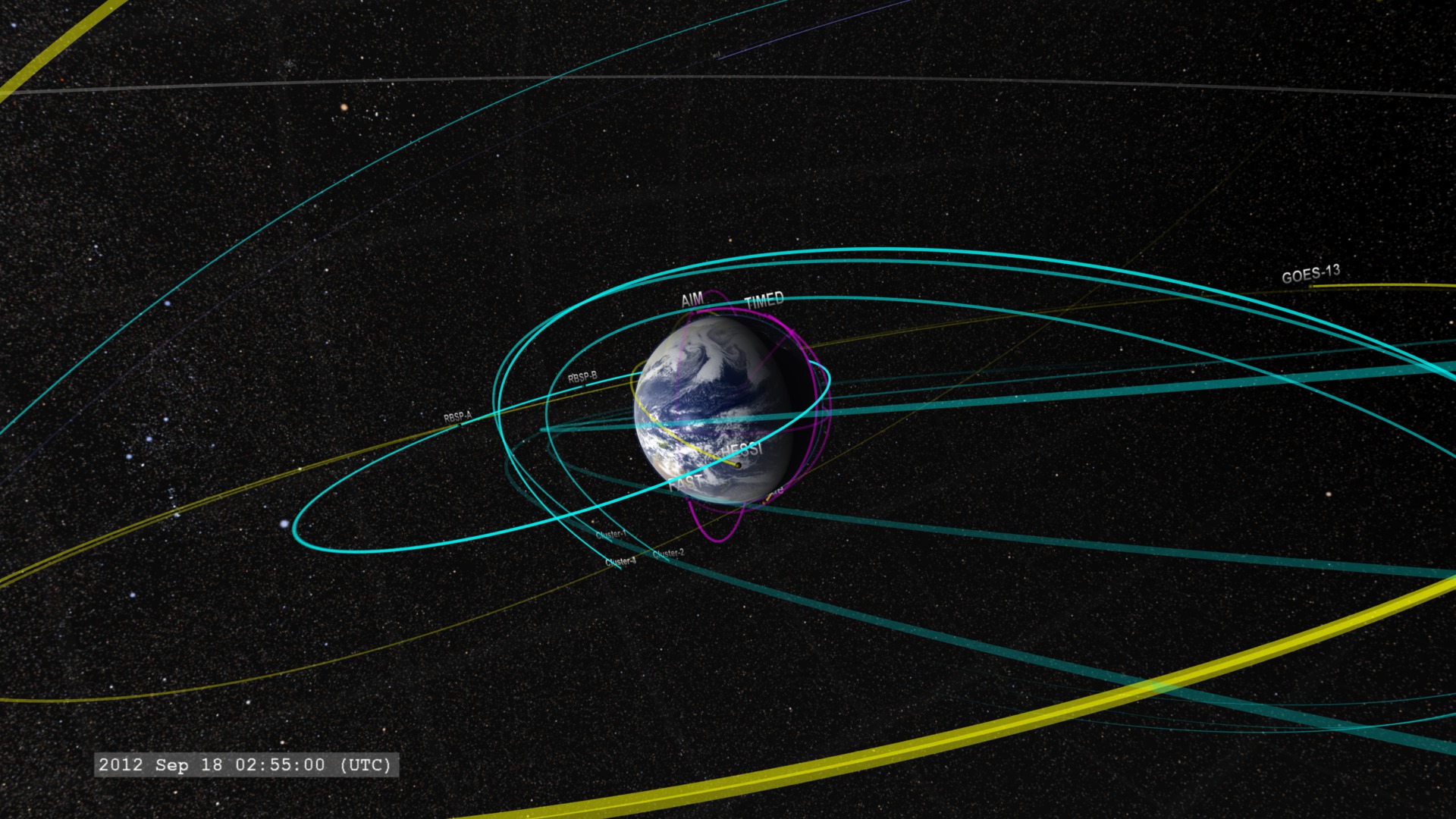
There've been a few changes since the 2012 Earth-Orbiting Heliophysics Fleet. As of Fall of 2013, here's a tour of the NASA Near-Earth Heliophysics fleet, covering the space from near-Earth orbit out to the orbit of the Moon.
The satellite orbits are color coded for their observing program:
Magenta: TIM (Thermosphere, Ionosphere, Mesosphere) observations Yellow: solar observations and imagery Cyan: Geospace and magnetosphere Violet: Heliospheric observations
Near-Earth Fleet:
- Hinode: Observes the Sun in multiple wavelengths up to x-rays. SVS page
- RHESSI : Observes the Sun in x-rays and gamma-rays. SVS page
- TIMED: Studies the upper layers (40-110 miles up) of the Earth's atmosphere.
- FAST: Measures particles and fields in regions where aurora form.
- CINDI: Measures interactions of neutral and charged particles in the ionosphere.
- SORCE: Monitors solar intensity across a broad range of the electromagnetic spectrum.
- AIM: Images and measures noctilucent clouds. SVS page
- Van Allen Probes: Two probes moving along the same orbit esigned to study the impact of space weather on Earth's radiation belts. SVS page
- TWINS: Two Wide-Angle Imaging Neutral-Atom Spectrometers (TWINS) are two probes observing the Earth with neutral atom imagers.
- IRIS: Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph is designed to take high-resolution spectra and images of the region between the solar photosphere and solar atmosphere.
Geosynchronous Fleet:
- SDO: Solar Dynamics Observatory keeps the Sun under continuous observation at 16 megapixel resolution.
- GOES: The newest GOES satellites include a solar X-ray imager operated by NOAA.
Geospace Fleet:
- Geotail: Conducts measurements of electrons and ions in the Earth's magnetotail.
- Cluster: This is a group of four satellites which fly in formation to measure how particles and fields in the magnetosphere vary in space and time. SVS page
- THEMIS: This is a fleet of three satellites to study how magnetospheric instabilities produce substorms. Two of the original five satellites were moved into lunar orbit to become ARTEMIS.SVS page
- IBEX: The Interstellar Boundary Explorer measures the flux of neutral atoms from the heliopause.
Lunar Orbiting Fleet
- ARTEMIS: Two of the THEMIS satellites were moved into lunar orbit to study the interaction of the Earth's magnetosphere with the Moon.
Movie showing the heliosphysics missions from near Earth orbit out to the orbit of the Moon.

Close-up view of the near-Earth heliophysics satellites.

Pulling out from Earth for a wider view...

One of the TWINS spacecraft come into view.

A wider view encompases the orbits of the Van Allen probes.

Passing geosynchronous orbit...

Passing through the magnetopause...

Cluster and THEMIS

The GOES satellites now include solar X-ray imagers.

A wide view of satellites in geosynchronous and geostationary orbits.

We're now out beyond the boundary of Earth's magnetosphere, where satellites more directly experience the influence of the solar wind.

Approaching the orbit of the Moon.

Passing the orbit of the Moon, we see the ARTEMIS spacecraft in lunar orbit.

The long-view of the near-Earth fleet.

Closing shot
Credits
Please give credit for this item to:
NASA's Scientific Visualization Studio, the NASA/Goddard Satellite Situation Center, and Space Track.
-
Animator
- Tom Bridgman (Global Science and Technology, Inc.)
Release date
This page was originally published on Monday, December 16, 2013.
This page was last updated on Sunday, November 12, 2023 at 10:19 PM EST.
Missions
This visualization is related to the following missions:Series
This visualization can be found in the following series:Datasets used in this visualization
-
SSCweb ephemerides (SSCweb)
ID: 538Satellite ephemerides
This dataset can be found at: http://sscweb.gsfc.nasa.gov
See all pages that use this dataset -
Space-Track TLE (Space-Track Two-Line Elements)
ID: 753Satellite ephemerides
This dataset can be found at: http://Space-Track.org
See all pages that use this dataset
Note: While we identify the data sets used in these visualizations, we do not store any further details, nor the data sets themselves on our site.