September 2007 Arctic Sea Ice vs 1979-2007 Average with Graph of 1979 to 2008 Ice Areas
Sea ice is frozen seawater floating on the surface of the ocean. Some sea ice is semi-permanent, persisting from year to year, and some is seasonal, melting and refreezing from season to season. The sea ice cover reaches its minimum extent at the end of each summer and the remaining ice is called the perennial ice cover. The 2007 Arctic summer sea ice reached the lowest extent of perennial ice cover on record. The area of the perennial ice has been steadily decreasing since the satellite record began in 1979, at a rate of about 10% per decade. But the 2007 minimum, reached on September 14, is about 38% lower than the climatological average. Such a dramatic loss has implications for ecology, climate and industry.
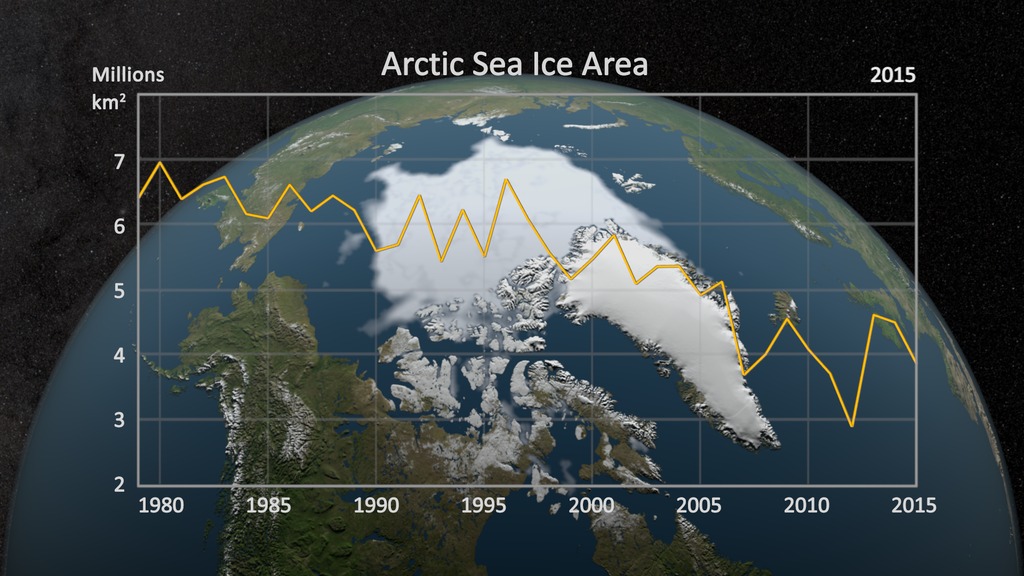
This image compares the difference between the perennial sea ice minimum area on September 14, 2007 and the 1979-2007 average minimum sea ice. A graph inset in the top left corner shows the decline in annual sea ice area from 1979 through 2008.

The sea ice image with labels and the graph inset

The sea ice image without labels and the graph inset

The graph inset
Credits
Please give credit for this item to:
NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center Scientific Visualization Studio
-
Visualizer
- Cindy Starr (Global Science and Technology, Inc.)
-
Animator
- Greg Shirah (NASA/GSFC)
-
Scientist
- Josefino Comiso (NASA/GSFC)
Release date
This page was originally published on Friday, January 9, 2009.
This page was last updated on Wednesday, May 3, 2023 at 1:54 PM EDT.
Datasets used in this visualization
-
[DMSP: SSM/I]
ID: 11Defense Meteorological Satellite Program Special Sensor Microwave Imager
See all pages that use this dataset -
[Nimbus-7: SMMR]
ID: 78 -
Comiso's September Minimum Sea Ice Concentration
ID: 540
Note: While we identify the data sets used in these visualizations, we do not store any further details, nor the data sets themselves on our site.