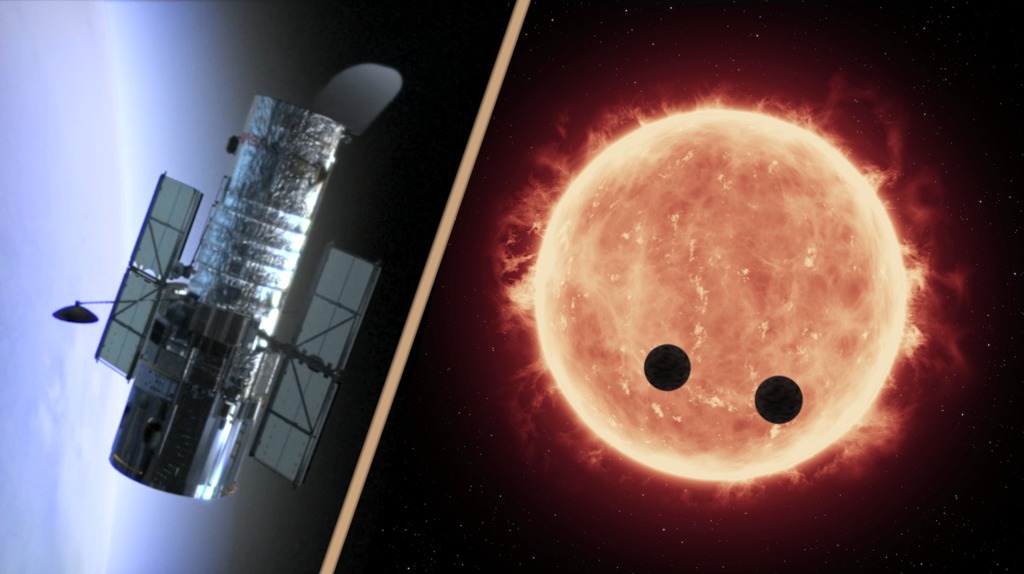
Hubble Finds Water Vapor On Distant Exoplanet
With data from the Hubble Space Telescope, water vapor has been detected in the atmosphere of a super-Earth within the habitable zone of its host star.
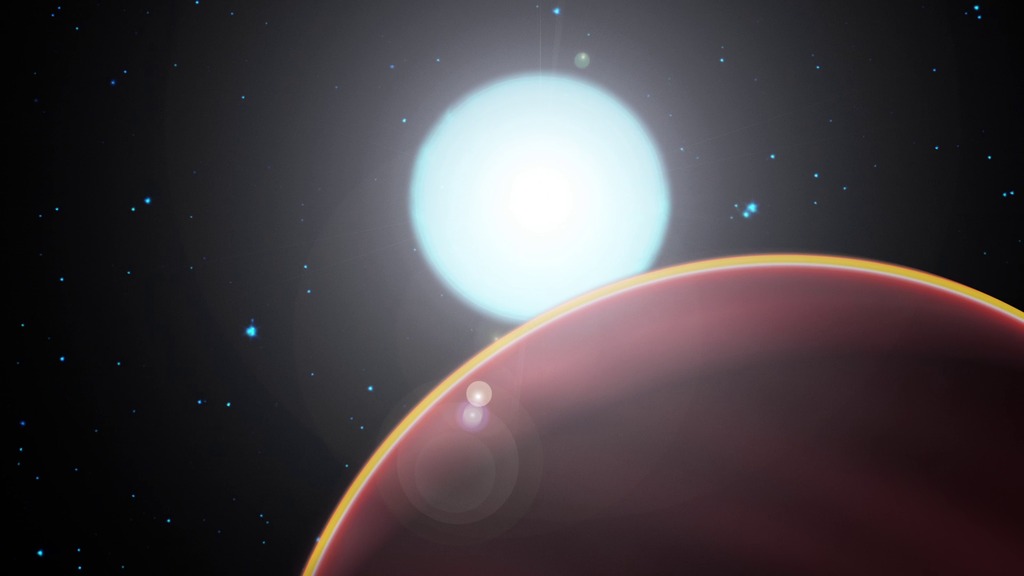
K2-18b, which is eight times the mass of Earth, is the only planet orbiting a star outside the solar system (or “exoplanet”) within the habitable zone.
For more information, visit https://nasa.gov/hubble.
Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center
Paul R. Morris (USRA): Lead Producer
Music credits: "Only Human" by Guillaume Bernard [SACEM]; Universal Production Music
Master version
Horizontal version. This is for use on any YouTube or non-YouTube platform where you want to display the video horizontally.
Square Version
This is a square 1:1 version of the video designed for Facebook or any other platform where you want to display a full-length square version of the video.
Vertical version
This vertical version of the episode is for IGTV or Snapchat. The IGTV episode can be pulled into Instagram Stories and the regular Instagram feed.
Textless version
Horizontal version without text. This is for use on any YouTube or non-YouTube platform where you want to display the video horizontally and need to add new text.
Credits
Please give credit for this item to:
NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center
-
Producer
- Paul R. Morris (USRA)
-
Technical support
- Aaron E. Lepsch (ADNET Systems, Inc.)
Release date
This page was originally published on Wednesday, September 11, 2019.
This page was last updated on Wednesday, May 3, 2023 at 1:45 PM EDT.









![Watch this video on the NASA Goddard YouTube channel.Music credit: "Deep Groove" by Danny McCarthy [ASCAP] and Thomas Dill [ASCAP]; Soundcast Music SESAC; Chronic Trax; Killer Tracks Production Music](/vis/a010000/a012800/a012844/hubble_trappist_2018-thumbnail.png)