Van Allen Probes Find Storage Ring in Earth's Outer Radiation Belt
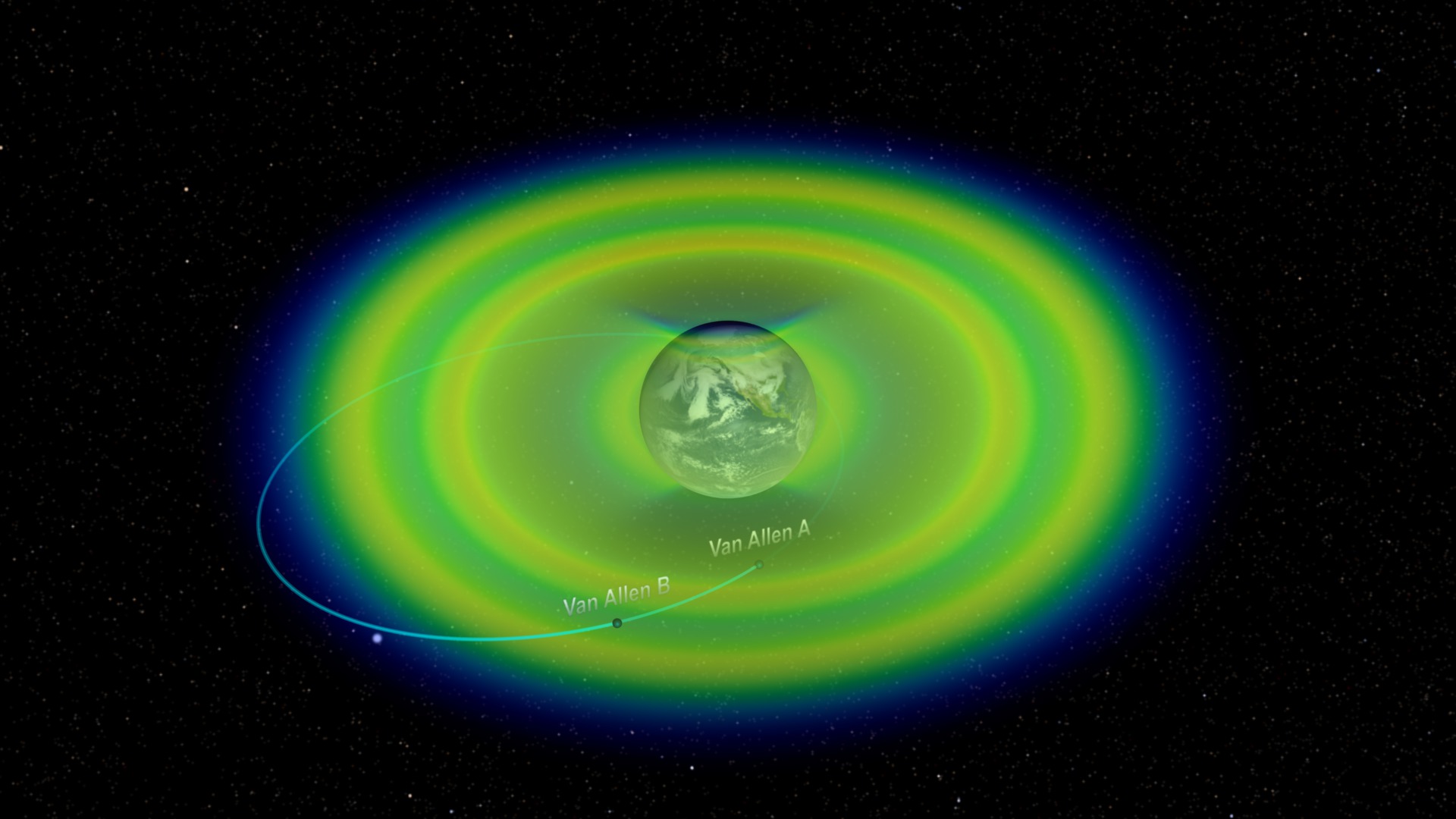
Since their discovery over 50 years ago, the Earth's Van Allen radiation belts have been considered to consist of two distinct zones of trapped, highly energetic charged particles. Observations from NASA's Van Allen Probes reveal an isolated third ring in the outer radiation belt.

Pictured from left to right: William Pickering, James Van Allen, Werner Von Braun holding up a model of Explorer 1 after its successful launch in 1958. Credit: NASARight: Van Allen and the discovery of the radiation belts, featured on the cover of Time magazine on May 4, 1959.
Credit: Time.

A cutaway model of the radiation belts with the 2 RBSP satellites flying through them. The radiation belts are two donut-shaped regions encircling Earth, where high-energy particles, mostly electrons and ions, are trapped by Earth's magnetic field. This radiation is a kind of "weather" in space, analogous to weather on Earth, and can affeThe inner belt extends from about 1,000 to 8,000 miles above Earth's equator. The outer belt extends from about 12,000 to 25,000 miles. This graphic also shows other satellites near the region of trapped radiation.
Credit: NASA

NASA's Living With a Star (LWS) program is a space-weather focused and applications driven research program. Its goal is to develop the scientific understanding necessary to effectively address those aspects of the connected sun-Earth system that directly affect life and society. The program is implemented by a series of inter-related science missions, space environment testbeds, and a targeted theory, modeling, and data analysis program. The Van Allen Probes are the second mission in the LWS program.
Credit: NASA
This two part movie shows an Aug. 31 coronal mass ejection (CME) from the sun , the same event that caused depletion and refilling of the radiation belts just after the Relativistic Electron-Proton Telescope (REPT) instruments on the Van Allen Probes were turned on. The first movie shows the CME as captured by NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO); the second shows several views of the same CME from the Solar and Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO).
Credit: NASA

This graph shows energetic electron data gathered by the Relativistic Electron-Proton Telescope (REPT) instruments, on the twin Van Allen Probes satellites in eccentric orbits around the Earth, from Sept. 1, 2012 to Oct. 4, 2012 (horizontal axis). It shows three discrete energy channels (measured in megaelectron volts, or MeV). The third belt region (in yellow) and second slot (in green) are highlighted, and exist up until a coronal mass ejection (CME) destroys them on Oct. 1. The vertical axis in each is L*, effectively the distance in Earth radii at which a magnetic field line crosses the magnetic equatorial plane.
Credit: LASP

Graphic with annotations.
Credit: LASP
One of the two Relativistic Electron-Proton Telescope (REPT) instruments for the Van Allen Probes is shown prior to and then during integration into the spacecraft in 2012. Each Van Allen Probe carries an identical suite of five instruments; REPT is part of the Energetic Particle, Composition, and Thermal Plasma Suite (ECT) aboard the Van Allen Probes.
Credit: JHUAPL

This long-term plot (approximately 12 years) from NASA's Solar Anomalous and Magnetospheric Particle Explorer (SAMPEX) spacecraft shows the established two-belt structure of the Van Allen radiation belts above the Earth. The L value is distance above the Earth. New, more advanced instrumentation on the Van Allen Probes has revealed a third belt.
Credit: NASA
This animation shows meridional (from north-south) plane projections of the REPT-A and REPT-B electron flux values. The animation first shows the expected two-belt Van Allen zone structure; from Sept. 3 through Sept. 6 only an intense belt of electrons remains and the inner zone and traditional slot region have not changed; next, the third 'storage ring' belt feature persists while a new slot region is seen and a completely new outer zone population has formed. Then, around Oct. 1, the storage ring feature remains while the outer zone decays away.
Credit: LASP
This visualization, created using actual data from the Relativistic Electron-Proton Telescopes (REPT) on NASA's Van Allen Probes, clearly shows the emergence of new third belt and second slot regions. The new belt is seen as the middle orange and red arc of the three seen on each side of the Earth. The twin Van Allen Probes launched on Aug. 30 2012.
Credit: JHU/APL, from REPT data/LASP

Radiation regions like the belts are found throughout our solar system and the universe. We are fortunate that we have this region of interest just a few thousand kilometers above the planet - it is like having our very own particle accelerator in the backyard. Here are four objects with radiation regions: The sun, Earth, Jupiter, and the Crab Nebula.
Credit: NASA/JHUAPL
This Sept. 28 coronal mass ejection (CME) from the sun, captured by NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO), is the event which caused the near total annihilation of the new radiation belt and slot region on Oct. 1.
Credit: NASA

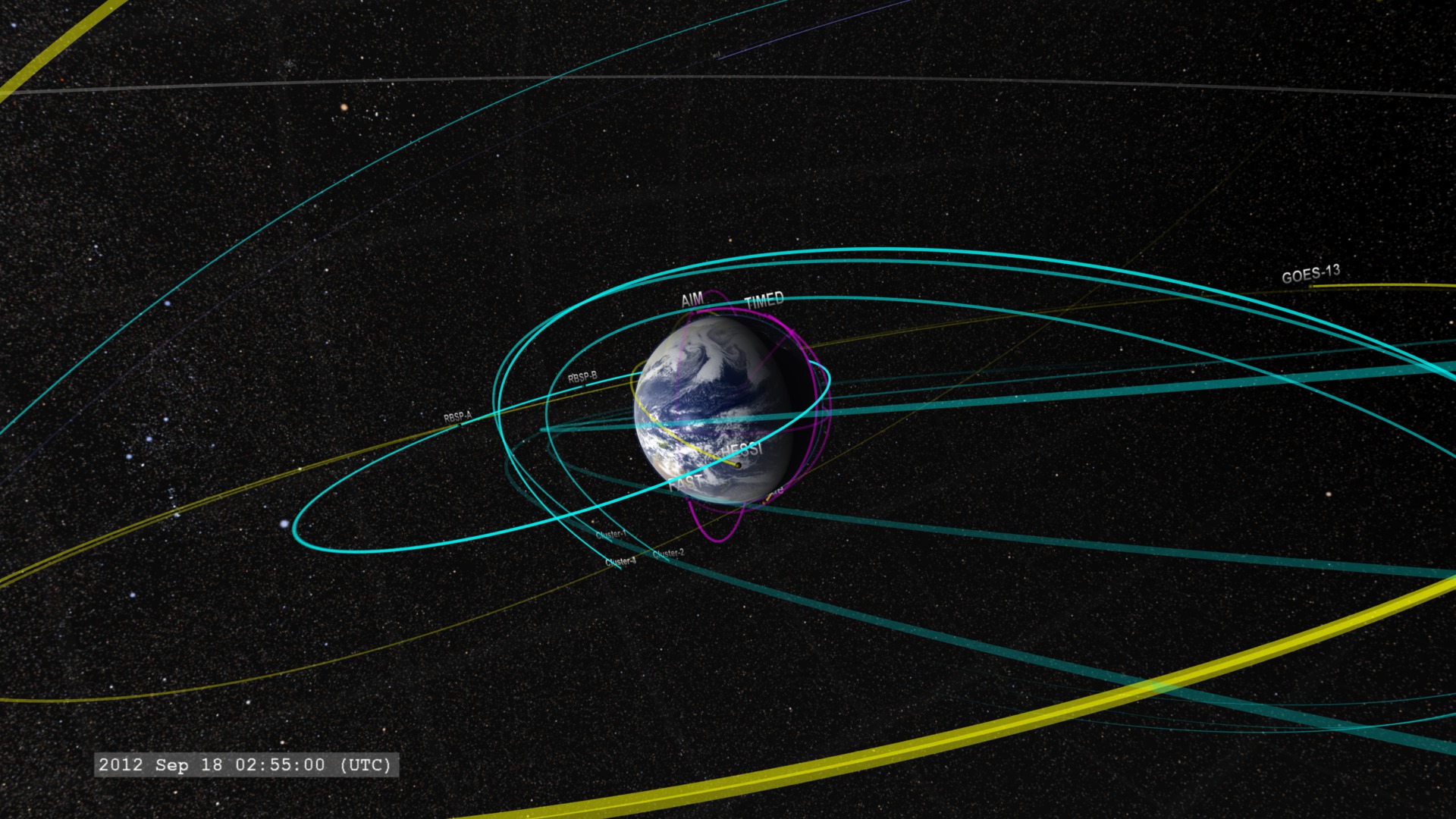
This movie shows NASA's Earth-orbiting heliophysics fleet as of 2013, from near Earth orbit out to the orbit of the moon. These missions study the thermosphere, ionosphere, and mesosphere; geospace and the magnetosphere; the heliosphere; and take solar observations and imagery. The Van Allen Probes (marked here as RBSP-A and RBSP-B) are in a highly elliptical orbit, shown in blue, around the Earth. Working as a team, these spacecraft provide the most comprehensive picture ever provided of how our sun interacts with our world.
Credit: NASA
To download the video, click here.
The Forecast Office of NOAA's Space Weather Prediction Center is the nation's official source of alerts, warnings, and watches. The office, staffed 24/7, is always vigilant for solar activity that can affect critical infrastructure.
Credit: NOAA.

The Space Weather Prediction Center has offered an email subscription service to customers both nationally and internationally since 2005. Now numbering over 32,000 subscribers, the satellite community accounts for about 9,500.
Credit:NOAA.

Satellite industry revenues globally have grown at about nine percent on average since 2006. In 2011, the last year for which data are available, the revenue was more than $177B (USD).
Credit: Satellite Industry Association.

Satellite anomalies of various types are the result of high levels of charged particles. The Van Allen Probes offer unique measurements of these populations for the benefit of satellite builders and operators.
Credit: JHUAPL
A narrated short video featuring visualizations of the Van Allen Belt's three ring structure. This video was not part of the news briefing, but is included in the associated feature story.
For complete transcript, click here.
For More Information
Credits
Please give credit for this item to:
NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center. However, individual items should be credited as indicated above.
-
Animator
- Tom Bridgman (Global Science and Technology, Inc.)
-
Video editor
- Genna Duberstein (USRA)
-
Narrator
- Karen Fox (ADNET Systems, Inc.)
-
Producer
- Genna Duberstein (USRA)
-
Scientists
- Shrikanth G. Kanekal (NASA/GSFC)
- Dan Baker (University of Colorado)
- Nicola Fox (NASA)
-
Writer
- Karen Fox (ADNET Systems, Inc.)
Release date
This page was originally published on Thursday, February 28, 2013.
This page was last updated on Wednesday, May 3, 2023 at 1:52 PM EDT.
Missions
This visualization is related to the following missions:Series
This visualization can be found in the following series:Tapes
This visualization originally appeared on the following tapes:-
Van Allen Probes Find Storage Ring in Earth's Outer Radiation Belt
(ID: 2013024)
Thursday, February 28, 2013 at 5:00AM
Produced by - Will Duquette (NASA)